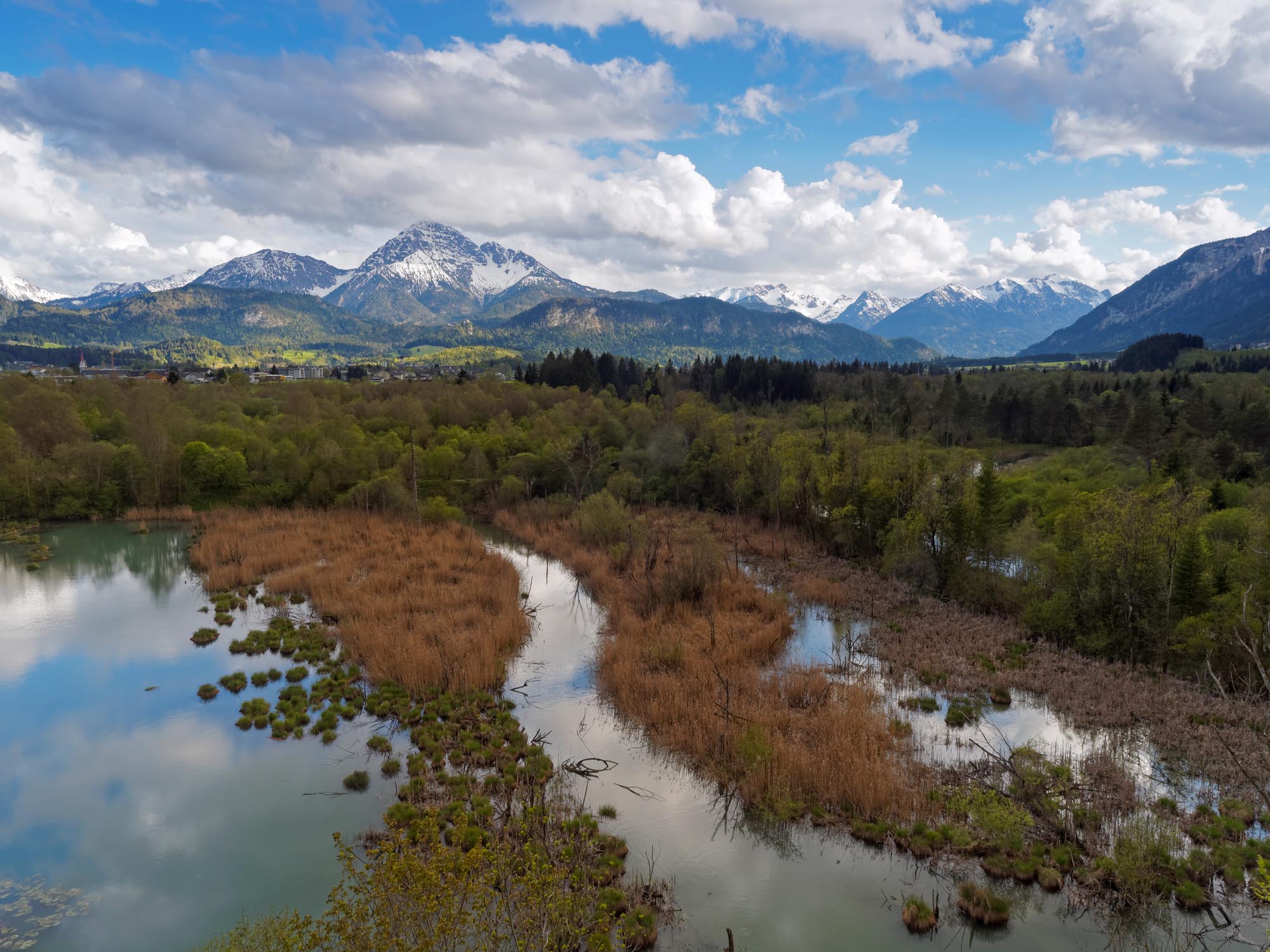
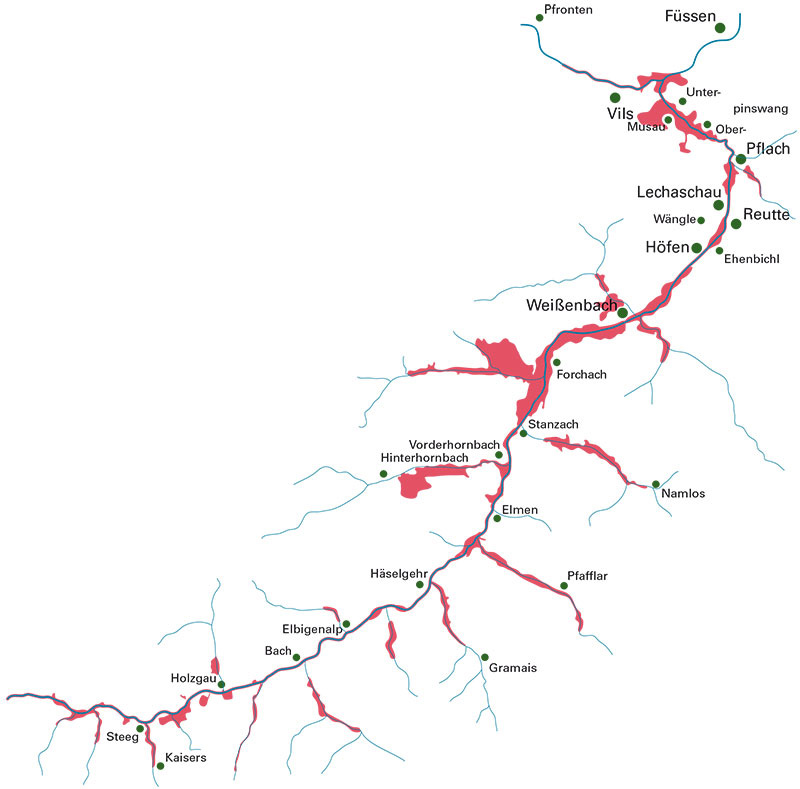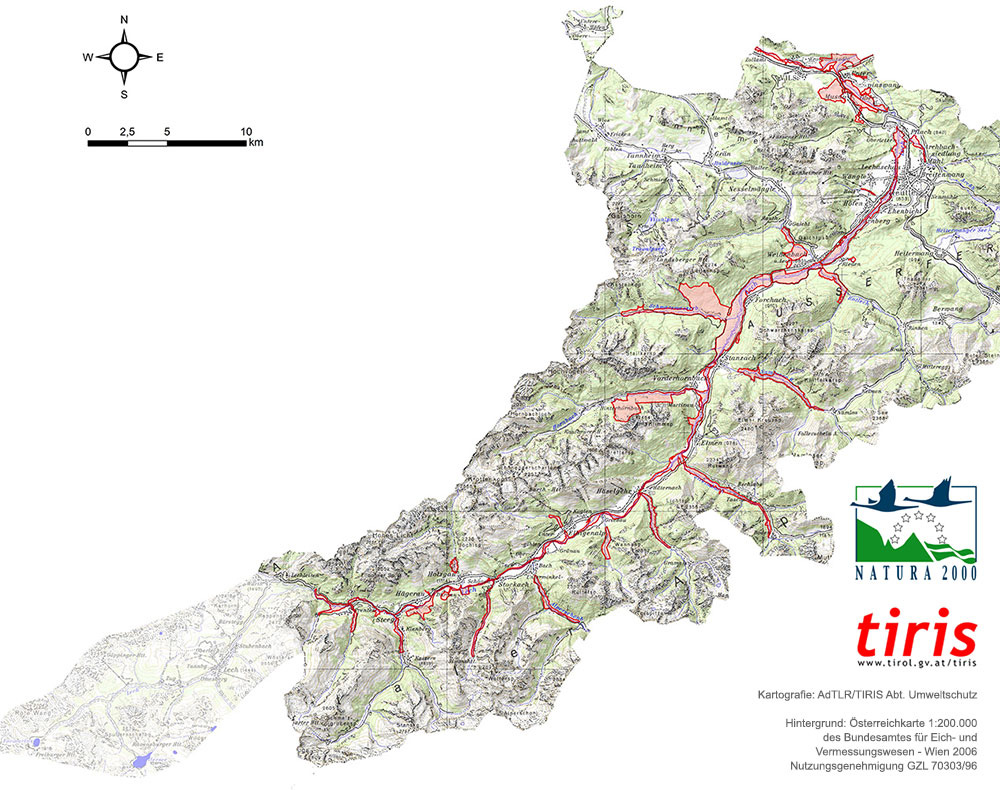
2000: Designation as Natura 2000 site (Flora-Fauna-Habitat & Birds Directive)
2001: Start of LIFE nature conservation project "Wild River Landscape Tyrolean Lech", investment sum: 7.78 million euros, 53 nature conservation measures
2004: Designation of the Tiroler Lech Nature Park by decree and designation as a nature reserve by the Department of Environmental Protection of the Province of Tyrol.
2006: Foundation of the Tyrolean Lech Nature Park Association with headquarters in Weißenbach
2007: Completion of the LIFE project.
2022: Completion of the 2nd LIFE project.